Embedded systems are specialized computing systems designed to perform dedicated functions or tasks within a larger system. Unlike general-purpose computers, embedded systems are tightly integrated into the devices they control, adding intelligence and automation. They are found in a myriad of applications, ranging from household appliances and automotive control systems to industrial machines and medical devices.
At the heart of many embedded systems lies a key component – the microcontroller.
The Role of Microcontrollers
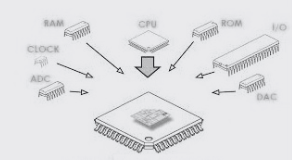
A microcontroller is a compact integrated circuit that contains a processor core, memory, and programmable input/output peripherals. These components work together to execute specific tasks, making microcontrollers the ideal choice for embedded systems due to their efficiency, size, and cost-effectiveness.
In the image above, you can see a simplified representation of a typical microcontroller. Let’s break down its components:
- Processor Core: This is the brain of the microcontroller, responsible for executing instructions.
- Memory: Both program memory (for storing the program code) and data memory (for storing variables and intermediate results).
- Input/Output Peripherals: These are the interfaces through which the microcontroller interacts with the external world. They can include GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output), serial communication ports, analog-to-digital converters, and more.
Why Embedded Systems Matter
Embedded systems have become an integral part of our daily lives, enhancing the functionality and efficiency of devices we use regularly. From the display panel on your microwave to the complex control systems in modern cars, embedded systems are everywhere.
Here are a few key reasons why embedded systems are essential:
- Dedicated Functionality: Embedded systems are tailored for specific tasks, allowing for optimal performance in a defined set of operations.
- Real-Time Operation: Many embedded systems require real-time responsiveness, making them suitable for applications where timely and accurate responses are crucial.
- Low Power Consumption: Microcontrollers are designed to operate efficiently, often with low power requirements, making them suitable for battery-powered and energy-efficient devices.
- Compact Design: The compact nature of microcontrollers allows for the creation of small and lightweight devices, contributing to the miniaturization trend in modern electronics.
If you would like to further know about what’s coming your way, please do use this link and show us your interest! Look forward to guide you through…https://link.growthflow.ai/widget/form/HmhohZk9HWIXV97CFlhT